Your Shopping Bag is Empty

The World Health Organization defines elder abuse as "a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust which causes harm or distress to an older person.”
Nowadays, cases of abuse of senior citizens are not uncommon. Elderly are being subject to excessive control and inadequate support, forced to sell off their property and leave their own houses to move into old age homes. What breaks our hearts is the fact that the "culprits" responsible for their condition are none other than their own children, blinded by the lust for power, wealth and materialism.
It is hard to accept the saddening truth about the condition of senior citizens in India – a country where children are more than welcome to live off their parents even after they are adults and where the blessings of the elders in the family are the laying stones of any new venture.
Even though it is the responsibility of daughters and sons to reciprocate the selfless love and care that they once received, due to the growing insensitivity, the duty has been passed on to the government and NGOs working for the welfare of the senior citizens in India. Several legal acts and policies have also been enforced to protect and empower the aged community in the country. However, all these efforts will only be able to reflect when people are made aware of their rights as the senior citizens of this nation.
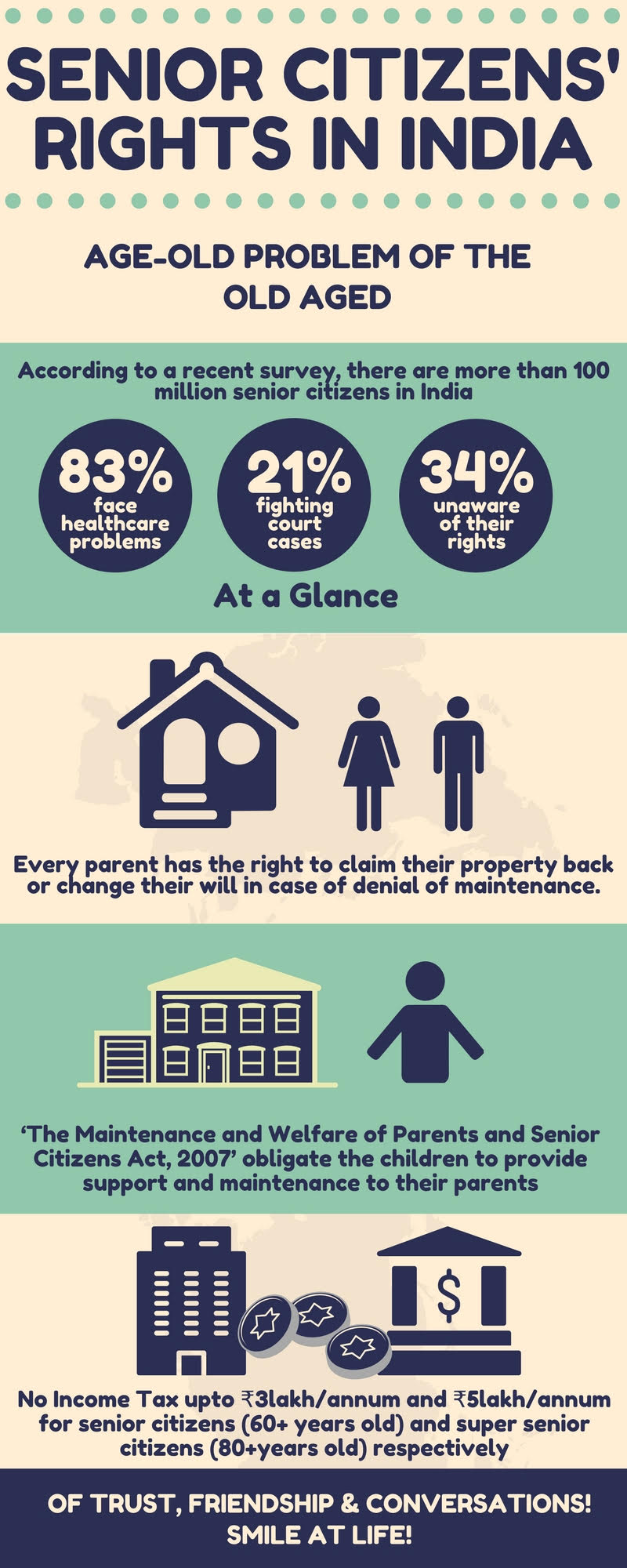
The Indian law provides constitutional protection under Article 41 and Article 46; by directing the state to secure the right of work and furnish public assistance to the people who have attained the age of 60 years or above. It is extremely necessary to make the senior citizens realize that help and justice exist.
‘The Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act, 2007’ was enacted to obligate children to provide support and maintenance to their parents. Even those seniors who do not have children can claim maintenance from their relatives or the persons who will inherit their property.
Under this act; a tribunal has been set up for speedy redressal of the cases filed against the infringement of the rights of people in their advancing years. The act also includes the provision of imprisonment and fines for those who abandon their parents or deny them their rights as awarded by the laws of the country. The order of the Tribunal can also be challenged in front of an Appellate Tribunal by filing an appeal within 60 days of such order passed by the former.
According to the Hindu and Muslim Law, the children, irrespective of their gender, cannot deny maintenance to their parents. Under Section 20 of ‘The Hindu Adoption and Maintenance Act’, it is the right of the parents to demand financial support even from their adopted children.
Although the Christian and Parsi Laws are silent about the issue, people, regardless of the community that they belong to, have the right secured under Section 125 of the Criminal Procedure Code (CPC). Even a married daughter is legally bound to help her parents, as required if she has the means to provide for their needs.
Savings:
The PMVVY scheme was recently extended from March 2018 to March 2020. The investment is capped at Rs. 15 lakh and gives a guaranteed 8 % fixed rate of return for a period of 10 years.
Insurance:
For seniors aged 60-80, national insurance offers the ‘Varishta Mediclaim Policy’ where the maximum sum insured is Rs. 1 lakh in case of hospitalization and Rs. 2 lakh for critical illnesses. LIC offers the Varishtha Pension Bima Yojana that provides assured pension for senior citizens.
Senior citizens get a tax exemption of Rs. 50,000 on health insurance premium under Section 80D. Exemption on medical expenditure for critical illnesses is Rs. 1 lakh for both senior citizens and super senior citizens.
Taxation:
Travel:
Miscellaneous Benefits:
As per Section 23 of the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizen Act 2007, when a person transfers a property to his/her son/daughter/relatives under the condition to provide maintenance to the former, he/she has the right to cancel such a transfer on the grounds that the latter refused to fulfill the conditions or denied the maintenance and amenities laid down under the conditions. Every parent has the right to claim their property back or change their will accordingly.
According to a recent survey, there are more than 100 million senior citizens in India. Many of them are living a life of humiliation and abuse due to lack of awareness about their basic civil rights. It is our duty to educate such people around us about their privileges and help them live a life of dignity. Let us not forget that we all will advance in age like our parents and our grandparents.
"Do unto others as you would have them do unto you" - may these words guide us ever.
By Tanshi Sahu
Guest Author and Student of Law
Bibliography
Senior Citizens' Guide, HelpAge India PDF | The Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizen Act, 2007, Ministry of Law and Justice PDF | Human Rights of Older People in India, Agewell Foundation PDF | Legal rights of senior citizens in India,
Disclaimer: The information in this blog post (“post”) is provided for general informational purposes only. While we have attempted to bring the best-known information to light, no reader of this post should act or refrain from acting on the basis of any information included in, or accessible through, this Post without seeking the appropriate legal or other professional advice. We request that the information contained in this post should not be construed as legal advice from Hey Zindagi Solutions Pvt. Ltd. or the individual author, as it is not intended to be a substitute for legal counsel on any subject matter.
Comments will be approved before showing up.